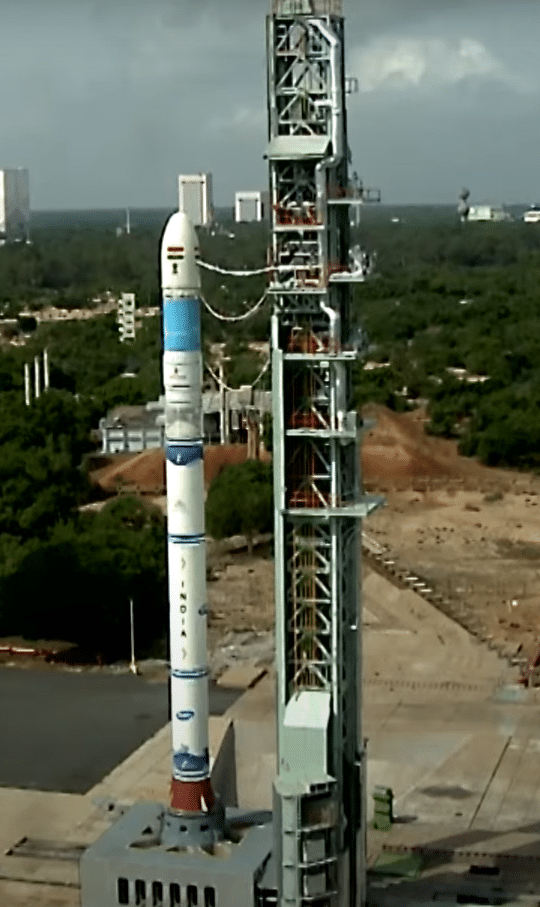
On August 16, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully launched the EOS-08 Earth observation satellite. The satellite was carried into orbit by the SSLV-D3 rocket, which lifted off at 9:17 AM from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota.

EOS-08: The New Era in Earth Observation
The EOS-08 satellite represents a major leap in satellite technology and Earth observation. Built on ISRO’s Microsat/IMS-1 platform, this satellite features advanced payloads and cutting-edge technology, underscoring ISRO’s commitment to innovation. It was launched using the Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV)-D3, marking a key milestone for both the satellite and the new launch vehicle.
Primary Objectives of the EOS-08 Mission
The EOS-08 satellite mission aims to demonstrate and test a variety of advanced technologies and payloads, highlighting both technological innovations and practical uses. The main goals of the mission are:
- The Electro-Optical Infrared Payload (EOIR) is designed to take images in both the Mid-Wave Infrared (MIR) and Long-Wave Infrared (LWIR) bands.
- Global Navigation Satellite System-Reflectometry Payload (GNSS-R) measures wind speeds and patterns over ocean surfaces. provides data on soil moisture levels, which is crucial for agricultural planning.
- SiC UV Dosimeter monitors ultraviolet irradiance and serves as a high dose alarm sensor for UV radiation. This measure UV radiation at the view port of the Crew Module for the Gaganayaan mission.
Features of EOS-08
- EOS-08 is equipped with advanced payloads that enable infrared observation, offering improved imaging capabilities for environmental monitoring and scientific research.
- The satellite includes a communication, baseband, storage , and positioning (CBSP) package, which combines several avionics functions into one system to simplify operations.
- The Dual Gimbal Antenna (Micro-DGA) ensures accurate communication and data transmission. The Phased Array Antenna (M-PAA) offers improved signal reception and transmission capabilities.
- Flexible solar panels efficiently collect energy while adjusting to the satellite’s design and structural constraints.

Parameter Specifications
- Orbit type: Circular Low Earth Orbit(LEO)
- Altitude: Approximately 475 km
- Inclination: 37.4 degree
- Expected Mission Duration: 1 Year
- Mass of the Satellite: 175.5 kg
- Power Consumption: Approximately 420 W
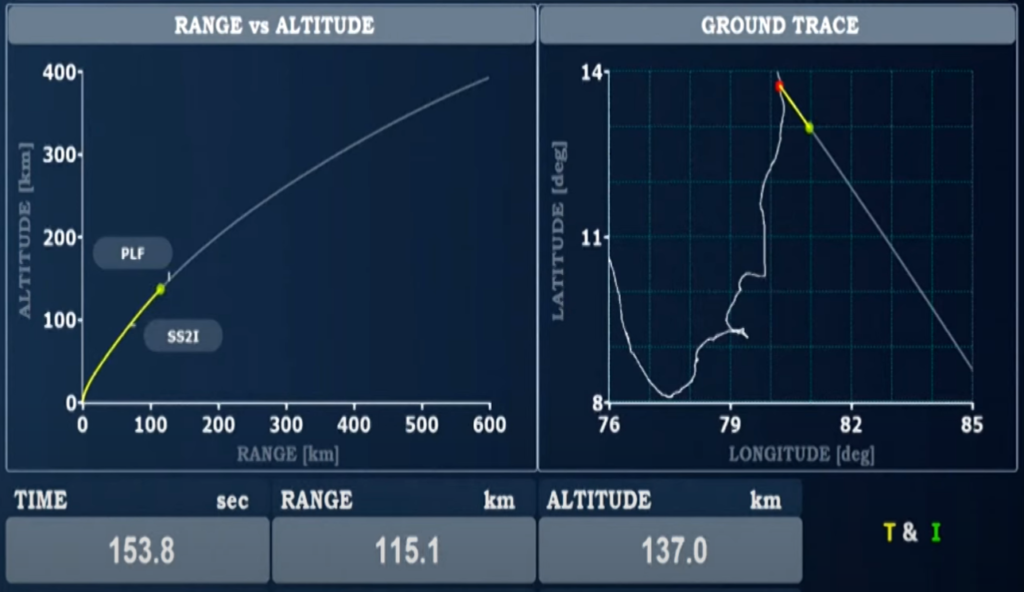
SSLV-D3 Vehicle Specifications
- The Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) is primarily used for missions like Developmental Flight 3, showcasing its ability to launch small payloads into low Earth orbit (LEO).
- Height of the vehicle is approximately 34 meters and diameter of the vehicle is around 2 meters.
- This vehicle is designed for rapid assembly and launch, allowing for shorter lead times compared to larger launch vehicles.
- SSLV-D3 is capable of accommodating various payload configurations and mission profiles.